
Apr 1 2016
By Jake Maki
This post has been republished with updates since its original publish date in November 2011
As we discussed in the preceding article, What is a VIN, there are two ISO documents that established the 17 digit VIN standard and the WMI section of the VIN. However, these documents were only recommendations. The VIN standard created by the NHTSA and enforced starting with the model year (MY) 1981, was required of all vehicles manufactured for use in the US and was much more stringent in its requirements.
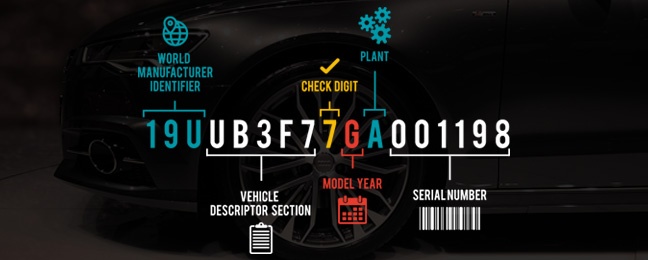
Like the ISO Standard, the NHTSA requires the VIN to be 17 digits long, with the first three digits reserved for the World Manufacturer Identification number (WMI) and the letters I,O and Q as illegal characters. In addition, the NHTSA required year (10th), manufacturing plant (11th) and a check digit (9th) be part of all VINs. (See table for comparison.) The remainder of this article will focus on the components of a VIN created to meet the NHTSA standard for the passenger and light duty vehicle segment.
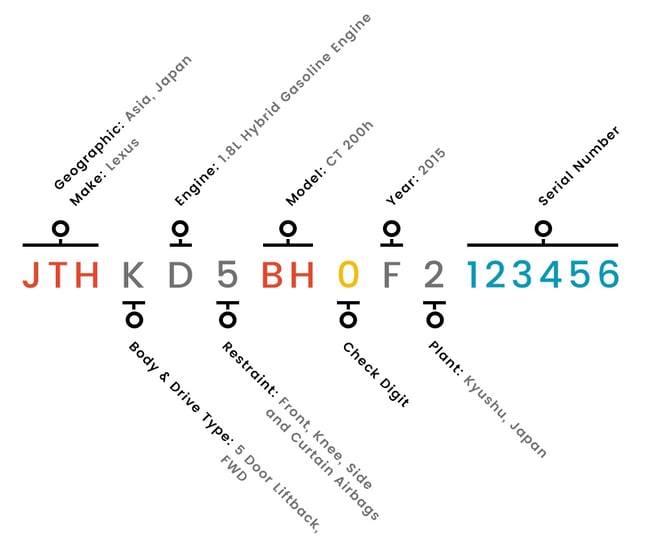
Example of VIN Breakdown:
Positions 1-3: World Manufacturer Identifier (WMI)
This is an alpha-numeric, three digit code that occupies positions one through three of the VIN. It identifies the manufacturer and country of origin of the vehicle. The first digit of the WMI tells you the general geographic area of manufacturer. The second designates the country of origin. The third digit designates the manufacturer. In addition, from 1981 to 2010 the third digit is used to indicate the category of vehicle.
For manufacturers producing < 500 of a given type of vehicle annually, the third digit of the WMI will be “9”, and will not uniquely identify the manufacturer. In these cases, the 12th -14th digits will also be assigned by a regulatory body, and will need to be considered along with the WMI to uniquely identify the manufacturer of the vehicle.
The fourth to eighth digits are set aside to capture descriptive elements of the vehicle. This is the meat of the VIN from a decoding standpoint. Almost all of the valuable information encoded in a VIN is found here. However, some elements of the vehicle captured are left to the manufacturer. Complicating things further, each manufacturer has a unique system of encoding information into the VIN. The type and quantity of information vary from manufacturer to manufacturer. However, some common data is always captured including model, engine, body type, drive type, restraint system and GVW Range(for Light Duty Vehicles and MPV's)
For MY2010 forward, all light duty/passenger vehicles are required to use the 4th digit to identify the category of vehicle.
The ninth digit of the VIN is used to provide a check digit that can be used to verify the validity of an encountered VIN using a calculation. The check digit can be any number between zero and nine, as well as “X” which represents the number ten for calculation purposes. VIN decoders use the check digit, along with validating characters I, O and Q, to determine if a VIN is valid. While only required in North America, it is utilized extensively abroad.
The model year is required to be captured in the 10th digit for all US vehicles. There are 30 characters approved for use in position 10 (I,O,Q,U,Z and 0 are excluded). Since the VIN Standard has been in use for over 30 years one should consider the 7th digit to determine the vehicles model year. If the 7th digit is numeric the model year is between 1981 and 2009. If it is an alpha character it is MY2010 or later.
The eleventh digit is used to identify the specific plant and plant location that the vehicle was manufactured in.
This is the sequentially assigned final portion of the VIN. In cases of small manufacturers, less than 500 vehicles annually, digits 12-14 are assigned to uniquely identify the manufacturer.
Proceed to the next article: VIN Decoding 101 Part 3: The Market Effect